The demand for ethical end-of-life vehicle (ELV) disposal and recycling has become more and more crucial as the world’s attention on environmental sustainability grows. An important step towards fostering sustainable automotive recycling and reducing the environmental impact of abandoned automobiles is the reason for setting up a Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility (RVSF). The main factors to consider and procedures to follow while setting up such facilities are described in this article.
The Voluntary Vehicle-Fleet Modernization Program (V-VMP) or “Vehicle Scrapping Policy” has introduced a mechanism for the environmentally friendly dismantling of unfit and polluting vehicles. Vehicles that have completed 15 years of age are termed End-of-Life Vehicles (ELVs). The Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility’s primary objective is to make sure that the ELVs are properly disassembled and disposed of to lessen their impact on the environment and enhance the utilization of recycled goods.
Disposing ELVs will lower the probability of road accidents and improve passenger safety on the road. This will also help people lower their maintenance expenses and improve the fuel efficiency of their vehicles. By dismantling the vehicle ethically, various parts and materials can be reused, and the remaining car body can be sent for recycling. By conducting these procedures as per the guidelines, the cost of manufacturing new vehicles will gradually decrease.
Before the policy launch, this market was operating in an unorganized manner. There were no suitable recommendations offered to ensure efficient operation and effective vehicle recycling. Now that the policy is in effect, these facilities must abide by the regulations governing environmental protection, the handling of dangerous materials, and effective waste management.
Steps to Set up a Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility (RVSF)
- Research and Business Planning: Before starting any business, thorough research and Business Planning are essential. The entrepreneur needs to research the policy, rules and regulations, licensing requirements, and environmental standards related to the disposal of ELVs in the region. A feasibility study will help the entrepreneur to understand whether to invest in the business or not. He will get the details of the project like what would be the payback period, rate of return on the investment, what would be the minimum amount required to start the business, working capital, and debt service credit ratio.
- Location and Infrastructure: The choice of location is an essential component for undertaking any business. The feasibility Study includes a detailed location analysis for the selected business considering various factors. Factors to consider when choosing a location include proximity to urban areas and major transportation corridors to facilitate logistics movement, the facility should be located where the transportation cost of the ELVs is minimal, and the supply could be on a daily basis depending on the number of ELVs procured for scrapping. The infrastructure of the facility should be built in such a manner to provide enough space for smooth movements of the vehicles and designated space for activities like dismantling, depolluting, and storage space for recyclable parts as well as for the vehicle.
- Obtaining License and Permissions: The first step towards setting up the registered vehicle scrapping facility is to apply for a license. For that purpose, the applicant should contact the Regional Transport Authorities. Understand the procedure for the application of necessary permits and licenses to operate legally. Permits for handling hazardous materials, disposing of garbage, and environmental compliance should be included. The facility will run safely and in compliance with established standards if these rules are followed. A feasibility Study or Feasibility Report would also include the list of licenses and permissions that are to be obtained for running this business.
- Equipment and tools: For safe and effective vehicle scrapping operations, certified depolluting, de-risking, safety, and health equipment are required. It is important to confirm that the apparatus satisfies safety requirements and can manage various vehicle types and sizes. The list of equipment is as follows:
- Hydraulic lifts
- Depolluting tools
- Hazardous Fluid Drainage Systems
- Dismantling tools
- Airbags Removal kit
- Forklifts and lifting equipment.
- Cutting tools
- Shredder
- Bailer
- Establishing Partnerships: To establish a network for the purchase of the ELV, partnerships with towing service providers, repair facilities, and insurance providers are required. To conduct business in the area successfully, relationships with the local government must be built. Engaging with these parties will assist in creating a dependable customer base and assure a steady flow of ELVs to the plant for scrapping. A relationship with the recycling facilities would also be advantageous since they will buy recyclable materials like plastic and scrap metal.
- Employee Training and Safety: The workers in the facility need to undergo training to perform their jobs satisfactorily. It is necessary to design safety processes and to adhere to safety precautions. Prioritizing workplace safety is crucial, as is ensuring that staff members are well-informed about the resources available to them for efficient task completion. To stay updated with changing laws and recommended industry practices for your field, you should offer regular training and refresher courses.
- Environmental responsibility: A registered vehicle scrapping plant should have environmental sustainability as one of its guiding principles. To handle hazardous materials including lubricants, gasoline, batteries, and other contaminants present in ELVs, implement appropriate waste management systems. It is important to ensure the correct disposal and recycling of collected items and establish cooperation with accredited recycling facilities. The aim is to reduce the amount of garbage dumped in landfills and increase ELV recycling rates.
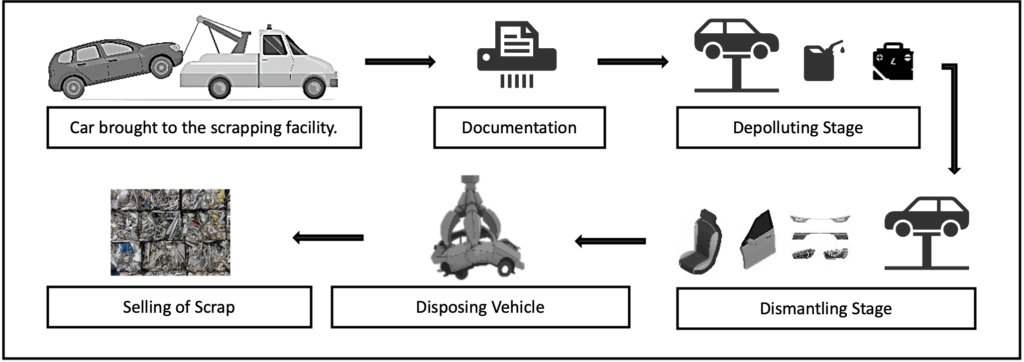
- Inspection and documentation: Each vehicle that arrives at the scrap yard is carefully inspected. The identity and ownership of the car are confirmed, and any required paperwork, including deregistration or ownership transfer, is finished.
- Depollution: Hazardous materials from the vehicles are securely removed to be disposed of or recycled properly. During this process, extra care is taken to prevent the discharge of dangerous compounds.
- Vehicle Dismantling: After hazardous materials and recoverable parts have been taken out, the remaining vehicle is methodically destroyed. This entails taking out elements that cannot be recycled or salvaged. The items that have been disassembled are divided into various waste streams for proper disposal or recycling.
- Scrap Metal Recovery: The main body of the car, which is made up of metal parts, is often crushed or shredded into smaller pieces for recycling. The valuable metals like steel, aluminum, and copper are subsequently recovered by further processing these components at a metal recycling facility.
- Recycling and Waste Disposal: According to municipal waste management standards, non-recyclable materials like plastics, upholstery, glass, and non-metallic parts are carefully sorted and disposed of. By sending these products to the proper recycling facilities, efforts are made to increase recycling rates.
How can a feasibility study or a Feasibility report help you decide whether to set up RVSF?
A feasibility study is a thorough examination and assessment of the viability and chances of success of a proposed project or enterprise. The feasibility study is carried out to ascertain whether the project is technically, economically, financially, operationally, environmentally, and legally feasible before investing substantial resources, such as time, money, and effort. Feasibility study for any project helps to answer a very basic but crucial question, “should we proceed with the proposed idea?”
Contents of a Feasibility Study Report:
- Executive summary
- Description of the project
- Technology considerations
- Marketplace for the project
- Marketing strategy
- Organization/staffing
- Project Schedule
- Financial projections
- Findings and recommendations
Aspects of a Feasibility Study:
Technical Aspect: This aspect of a feasibility study or a Feasibility Report evaluates whether the proposed project can be technically implemented. Technology, infrastructure, and resources required for the project are readily accessible or not. It looks at the project’s technical requirements, potential restrictions, and any prospective technological challenges that may arise. It also studies the current technology as well as the scope for future technological advancements that will lead to the growth of the business.
Economic Aspect: The economic aspect of the feasibility study evaluates the project’s viability from a broader economic perspective. How the project will affect market circumstances, stakeholders, and the economy at large. A feasibility study will take into consideration variables including market demand, the project’s economic impact on society, the project’s social and environmental impact on the environment and natural resources, sustainability, and corporate social responsibility.
Financial Aspect: This involves the financial viability, sustainability, and profitability of the project. It involves computing the project’s estimated expenses, including resource requirements, operational costs, capital expenses, and maintenance costs, and estimations of revenue are developed. Additionally, it analyses the financial metrics for the project, including profitability ratios, internal rate of return (IRR), payback period, net present value (NPV), as well as return on investment (ROI).
Operational Aspect: This aspect of the feasibility study involves understanding the business and operating model. Processes and workflows are designed. People required for operating the business (white collar and blue collar), skills needed in such manpower, and training requirements if any are identified. Various utilities and consumables are required, and logistics for the business are configured.
Environmental Aspect: The environmental aspect of a feasibility study or a feasibility report examines the potential impacts of a project on the environment and evaluates its sustainability. It emphasizes recognizing and comprehending environmental laws and regulations, limiting any negative consequences the project might have on ecosystems, natural resources, and the environment, and ensuring legal and regulatory compliance. It entails assessing potential habitat fragmentation, resource depletion, deforestation, and soil erosion impacts and developing countermeasures.
Legal Aspect: The legal and regulatory aspect of a feasibility study or a Feasibility Report examines the project’s compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and standards. It entails identifying and understanding the permissions, licenses, and certifications that are legally required for the project. This attribute makes sure the project can function within the law and steer clear of any legal or regulatory difficulties.
Our Team of highly experienced and reputed consultants having Big-4 consulting experience have undertaken/performed numerous feasibility studies over the years and helped businesses arrive at a conclusive decision. We will be happy to help and guide any existing business/entrepreneurs/family business/companies wanting to set up RVSF in India or any other business.
To know more about Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility (RVSF), click here.
