In a landmark development that reshapes global economic rankings, India has officially overtaken Japan to become the world’s 4th largest economy in 2025. With a nominal GDP of USD 4.187 trillion, India is now only behind the United States, China, and Germany. What’s even more remarkable is that this achievement comes ahead of schedule, defying earlier projections set for 2027.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) confirmed this shift in its April 2025 World Economic Outlook report. It also highlighted India’s rising status as the fastest-growing major economy, powered by robust reforms, digital innovation, and a youthful workforce.
India Overtakes Japan: Confirmed by IMF and Government Officials
According to NITI Aayog member Arvind Virmani, India is well on track and “in the process” of solidifying its place as the fourth-largest economy by the end of 2025. While official full-year data will be available early in 2026, Virmani expressed confidence, saying: “We need full-year GDP data to officially confirm it, but I’m confident India will end 2025 ahead of Japan.”
NITI Aayog CEO B.V.R. Subrahmanyam went further, stating that: “As I speak, India is already the world’s fourth-largest economy with a GDP exceeding USD 4 trillion.”
The IMF’s data backs this up:
- India: USD 4.187 trillion
- Japan: USD 4.186 trillion
- United Kingdom: USD 3.839 trillion
Global GDP Rankings 2025
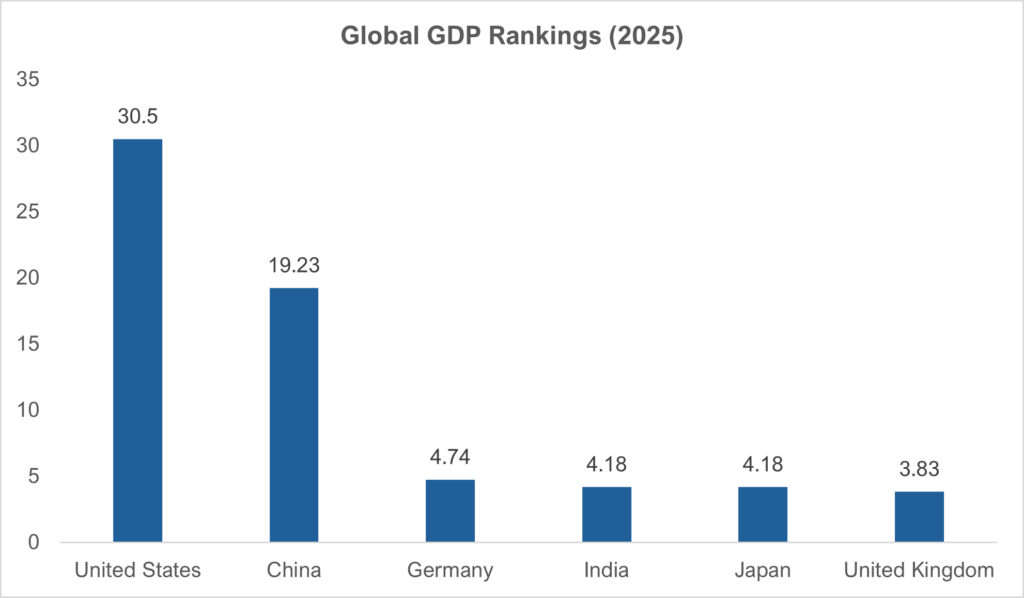
| Rank | Country | GDP (USD Trillion) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States | 30.507 |
| 2 | China | 19.231 |
| 3 | Germany | 4.744 |
| 4 | India | 4.187 |
| 5 | Japan | 4.186 |
| 6 | United Kingdom | 3.839 |
India’s meteoric rise is not only a reflection of economic policies and reforms but also of its growing influence on global markets. The trajectory from fifth to fourth-largest economy in just a few years illustrates the power of compounding growth and macroeconomic stability.
IMF, World Bank and UN: India’s Economic Outlook Is Bright
The IMF describes India as the “only bright spot” in a global economy that has been weighed down by inflation, conflicts, and slowing trade. The 2023 World Economic Outlook predicted India would be a key contributor to global growth in the coming years.
Likewise, World Bank Country Director for India, Auguste Tano Kouame, remarked in early 2025: “India is the shining light in the world.” A recent United Nations (UN) report, World Economic Situation and Prospects (WESP), also singled out India as the only major economy growing at a consistent pace, despite global slowdowns.
India’s Growth Rates Outshine Other Major Economies
The EY economic report for 2022–2028 reveals India has the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) among major economies in both nominal GDP and PPP terms.
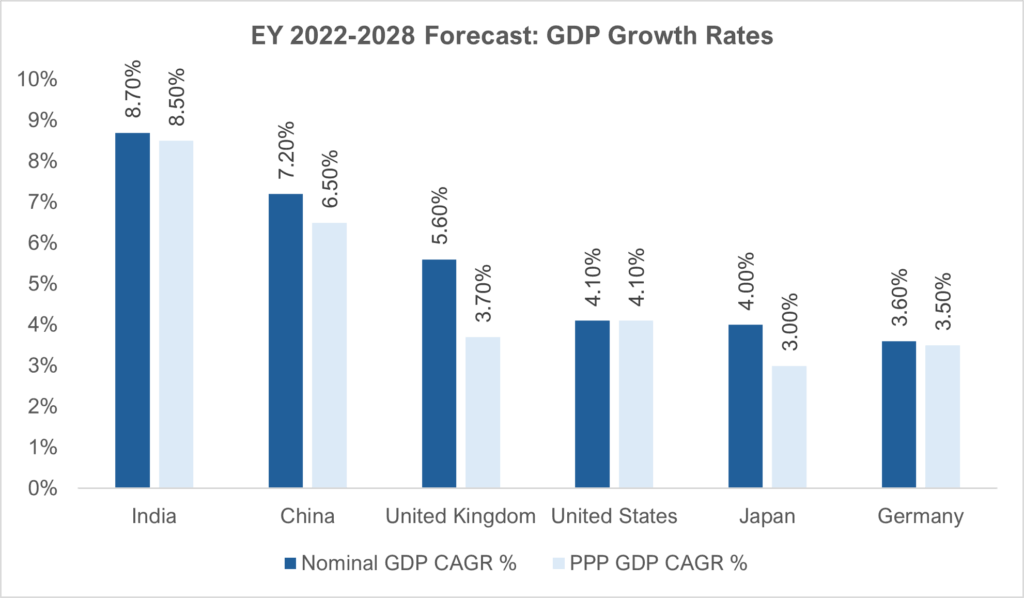
| Country | Nominal GDP | PPP GDP |
| India | 8.70% | 8.50% |
| China | 7.20% | 6.50% |
| UK | 5.60% | 3.70% |
| US | 4.10% | 4.10% |
| Japan | 4.00% | 3.00% |
| Germany | 3.60% | 3.50% |
These numbers aren’t just impressive – they point to India becoming the third-largest economy by 2028, if not earlier, with GDP forecasts as high as USD 5.7 trillion by that time.
India in PPP Terms: Already Third, Closing in on China
In Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) terms – which adjust for price level differences between countries – India is already the third-largest economy, ahead of Japan and Germany.
The EY report notes:
- India’s PPP economy is adding USD 7.5 trillion by 2028.
- This growth is equivalent to Japan’s entire current annual PPP output.
- By 2028, India will narrow the gap with China by 2 percentage points of global output.
By 2027, the US economy will be only 1.7 times larger than India’s in PPP terms, a staggering change from past decades.
A March 2025 analysis by Morgan Stanley forecasts that India will:
- Reach USD 4.7 trillion in GDP by 2026.
- Surpass Germany to become the third-largest economy globally by 2028.
- Increase its share of world GDP from 3.5% to 4.5% by 2029.
Given India’s current growth pace, these milestones could arrive sooner than expected.
Factors Driving India’s Economic Success
- Pro-Business Reforms: Reforms like Goods and Services Tax (GST), Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, and digitization efforts have made doing business in India easier.
- Demographic Dividend: India has one of the youngest populations globally, with over 65% under 35 years. This supports a dynamic labor force and growing consumption.
- Infrastructure and Digital Push: Massive investments in highways, smart cities, and digital infrastructure have improved logistics and financial access across the country.
- Political Will abd Stability: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s administration has set clear economic goals – including making India a developed economy by 2047, with a USD 35 trillion GDP target.
Looking Ahead: India’s $35 Trillion Vision by 2047
The Indian government aims to transform the nation into a developed economy by its 100th year of independence in 2047. Key objectives include:
- Boosting manufacturing and exports
- Becoming energy self-reliant
- Leading in clean tech and AI innovation
- Elevating per capita income significantly (which is already projected to double from USD 1,438 in 2013-14 to USD 2,880 by 2025)
This long-term vision is supported by strong macroeconomic fundamentals, rising global investment interest, and a large domestic market.
India’s ascent to the fourth-largest economy in the world in 2025 is not only a proud moment but a critical indicator of the nation’s growing influence. Surpassing Japan well ahead of projections shows that India is no longer an emerging economy – it’s an emerging superpower.
With world-leading growth rates, widespread institutional confidence, and transformative reforms, India is on track to become the third-largest economy by 2028 and aims to be a USD 35 trillion economy by 2047.
The message is clear: the global economic narrative is changing – and India is writing the next chapter.
Credits: DD News, Economic Times
Read More: $5 Trillion Economy: India’s Economic Growth Strategies, Challenges, and Future Prospects
