Introduction
Hydrogen can contribute towards the decarbonization of the global economy as it is a versatile source of energy which can be produced using low carbon emitting sources. The Government of India is determined to use Hydrogen as fuel and feedstock in the coming future. The objective of this article is to provide highlights of the National Green Hydrogen Mission, Policy and Regulations, Financing options for Green Hydrogen, and the Pilot projects in India.
Why is India betting big on hydrogen?
- To secure the country from the fluctuations in the prices of fuels as well as find alternatives to strengthen its National Energy Security.
- India produces approx. 7% of the global CO2 emission after China and the US. India tends to reduce 45% of the emissions by 2030.
- India wants to become economically independent and improve its balance of trade as it is the third largest importer of crude oil.
The factors contributing towards India’s aim to become the world leader are mainly:
- Availability of abundant and cheap Renewable Power
- Legislative Support
- Grid Stability
- Coastline and ports
- Engineering, Procurement & Construction capability
National Green Hydrogen Mission
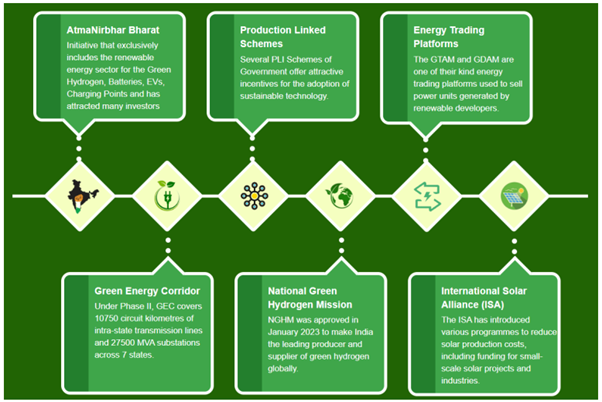
The National Green Hydrogen Mission of India aims to achieve energy independence by 2047 and Net Zero emissions by 2070, recognizing the pivotal role of Green Hydrogen. India, with abundant renewable energy resources, aims not only to meet its domestic energy needs but also to become a global supplier of Green Hydrogen. Currently, India imports over 40% of its primary energy, costing over USD 90 billion annually, with key sectors like mobility and industrial production heavily dependent on these imports.
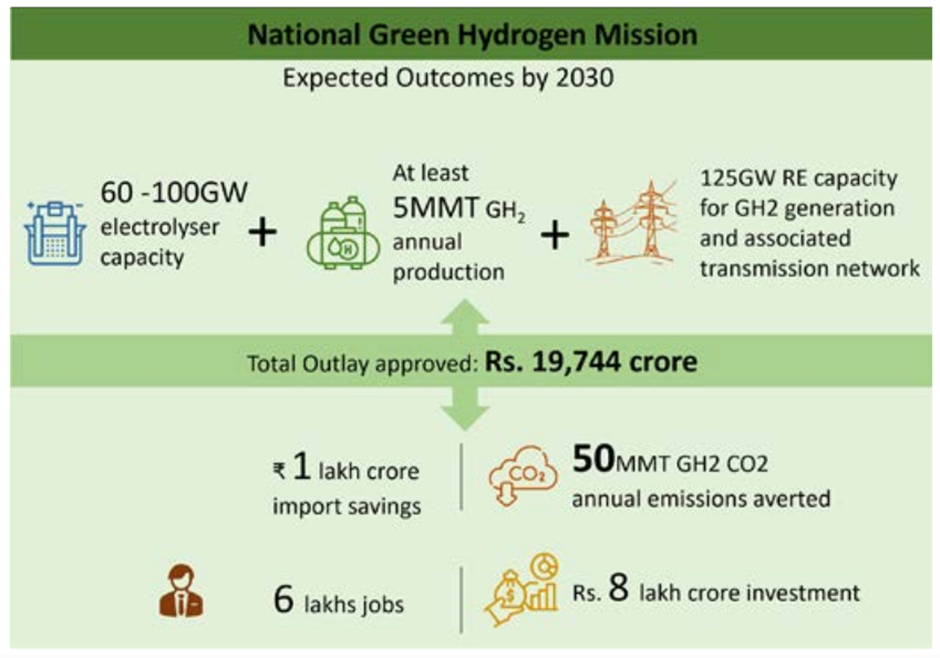
The mission, approved by the Union Cabinet on January 4, 2023, has an initial outlay of Rs. 19,744 crores. This includes Rs. 17,490 crores for the Strategic Intervention for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme, Rs. 1,466 crores for pilot projects (covering low carbon steel, mobility, and shipping projects), Rs. 400 crores for research and development, and Rs. 388 crores for other mission components. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has formulated guidelines for the implementation of these components.
Expected outcomes by 2030 include:
- Green Hydrogen production capacity of at least 5 million metric tonnes per annum.
- Over Rs. 8 lakh crores in total investments.
- Creation of over 600,000 jobs.
- Reduction in fossil fuel imports worth over Rs. 1 lakh crore.
- Abatement of 50 million metric tonnes of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
The mission’s governance structure includes an Empowered Group (EG) chaired by the Cabinet Secretary, an Advisory Group (AG) chaired by the Principal Scientific Advisor, and a Mission Secretariat within MNRE. The mission will be implemented in phases, initially focusing on deploying Green Hydrogen in existing hydrogen-using sectors and developing an ecosystem for research, development, regulations, and pilot projects, with later phases expanding this scope.
Enabling Policies and Regulations
The Government of India is playing a crucial role in fostering the development and adoption of Green Hydrogen in India. Recognizing the importance of a supportive policy framework, various policy instruments and regulatory measures are designed to create a conducive environment for Green Hydrogen production and utilization.
Key Policies and Initiatives
- Inter-state Transmission Charges Waiver for 25 years for projects commissioned by December 2025.
- Exemptions from prior environmental clearances.
- All consumers can use Green Energy and are exempted from cross-subsidy charges, additional surcharges, and favorable banking provisions.
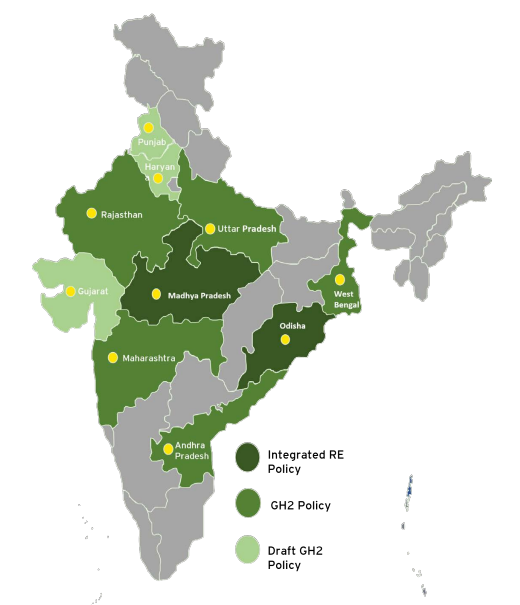
State Specific Policies
Several Indian States have formulated specific policies to encourage Green Hydrogen production and utilization. These states include Maharashtra, Odisha, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Financing Green Hydrogen – Bridging the Gap
The development and deployment of Green Hydrogen Projects in India is supported by various financing mechanisms. Given the capital-intensive nature of these projects, innovative and diverse financing options are crucial to bridge the investment gap and accelerate growth in this sector.
Key Financing Opportunities
- Public – Private Partnerships
- Government Subsidies and Grants
- Low-cost financing from Multilateral Agencies
- Carbon Financing and Carbon Credits
- Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) and Green Bonds
- Export Credit Agencies
- Venture Capital and Private Equity Investments
- Innovative financing mechanisms
- IREDA (Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Ltd)
Key Enablers of Financing
Strategic Financial Instruments
- Green Bonds
- Equity and Debt Financing
- Innovative Financial Instruments
Pilot Projects – Leading the Way
India is becoming a leader in Green Hydrogen development, driven by goals for energy independence and decarbonization. The National Green Hydrogen Mission, launched in 2023 with a budget of ₹19,744 crore, is advancing projects across various sectors such as mobility (road, locomotive, aviation), shipping, steel, and domestic cooking gas blending. It also supports manufacturing components like electrolysers and cylinders. Notable projects include Jindal Stainless’ plant in Hisar and SJVN’s pilot project in Himachal Pradesh. Upcoming projects by companies like NTPC, NHPC, IOCL, L&T, GAIL, ACME, THDC, and Indian Railways further boost production. Government incentives aim to achieve 5 million metric tonnes of Green Hydrogen annually by 2030, paving the way for a sustainable future.
Export-oriented Agreements
- ACME and IHI Corporation: ACME to supply 0.4MMTPA of Green Ammonia to Japan’s IHI Corporation from a project in Gopalpur, Odisha, starting in 2027.
- Sembcorp India: Collaborating with Sojitz Corp and Kyushu Electric Power Co to export green ammonia from India to Japan.
- NTPC in Andhra Pradesh: Setting up India’s largest Green Hydrogen production facility in Visakhapatnam.
- Yara and ACME: Long-term agreement for reduced CO2 ammonia supply from ACME to Yara.
- JERA and Renew: Developing a green ammonia production project in India.
Green Hydrogen Projects for Microgrid
- SJVN: Commissioned a green hydrogen fuel cell-based microgrid at NJHPS, Himachal Pradesh.
- NHPC: Awarded a pilot project for a green hydrogen fuel cell microgrid at Nimmo Bazgo Power Station, Leh.
Green Hydrogen Projects for Mobility
- NHPC in Kargil: Developing a 500-kW solar power project to support a hydrogen refueling station.
- Indian Railways: Pilot project to retrofit diesel locomotives with hydrogen fuel cells, starting with the Jind-Sonipat route.
- NTPC in Greater Noida: Executing an integrated hydrogen refueling station for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) buses.
- Oil India Limited in Assam: Commissioned a pure green hydrogen pilot plant in Jorhat.
- Oil India Limited in Himachal Pradesh: Establishing a 1 MW green hydrogen project.
- Indian Oil R&D Centre, Faridabad: Producing green hydrogen to power buses in the NCR.
- Indian Oil Project in Leh: Setting up a hydrogen refueling station and solar plant.
- Cochin Shipyard Limited: Developing India’s first hydrogen fuel cell ferry and a zero-emission feeder container vessel.
Green Hydrogen Project for Steel
- Jindal Stainless, Hisar: Hygenco India Private Limited established a green hydrogen plant to significantly reduce carbon emissions.
Green Hydrogen Project for the Domestic Sector
- NTPC Project in Kawas: Commissioned the country’s first green hydrogen blending project with piped natural gas.
- Torrent Power in Gorakhpur: Implementing a pilot project for green hydrogen blending in the city gas distribution network.
- ATL Gas Blending Project in Ahmedabad: Adani Total Gas Ltd blending green hydrogen with natural gas for residential and commercial use.
- NTPC Energy Technology Research Alliance: Developed a hydrogen burner for cooking, demonstrating a clean alternative to traditional fuels.
Note: All the projects have not been mentioned here in the booklet. However, there are more than 50 projects,
consisting of pilot and commercial production projects, which are in different stages of planning, tendering,
implementation and commissioning.
This article is the second part of the 2-part series of Green Hydrogen Revolution in India. It is a summary of the INDIA’S GREEN HYDROGEN REVOLUTION – An Ambitious Approach Report published jointly by MNRE and EY.
This article is the second part of the 2-part series of Green Hydrogen Revolution in India. The first part is linked here.
